You’ve probably interacted with AI a dozen times already today. It’s the silent curator behind your Netflix queue, Smart image editors, the helpful navigator in your mapping app, and the increasingly intelligent voice assistant on your and countless other technologies woven into our daily lives. Artificial Intelligence is no longer a sci-fi fantasy you have seen as Iron Man’s Jarvis; it’s the foundational technology of our modern world.
But what is it, really? How does a machine actually “think”?
This article will help you understand the working. We’ll start with the absolute basics, dive deep into the engine room of Generative AI, and explore its profound impact on our world, backed by hard data. Let’s unbox the mind of the machine.
Part 1: What is AI? The Big Picture 🖼️
At its heart, Artificial Intelligence is the science and engineering of making machines smart. The goal is to create systems that can perceive their environment, think, learn, and take actions to solve complex problems, much like a human does, or in easy words making a machine capable enough to think like a Human- Mimic the human, The best creature of God (as mentioned in various religious books)
It’s not magic; it’s about learning from data. Imagine teaching a child to recognize a dog. You don’t write a long list of rules (“if it has fur, four legs, and a tail, it’s a dog”). Instead, you show them many, many pictures and real-life examples of dogs. Over time, their brain learns to identify the patterns that define “dog”.
Modern AI works in a very similar way, but on a colossal scale. It learns from vast datasets—terabytes of text, images, sounds, and code—to recognize patterns far too complex for any human to define manually.
The engine driving this revolution is a subfield of AI called Machine Learning (ML), and more specifically, a powerful technique which is a subfield of ML itself is called Deep Learning. Deep Learning uses complex structures called neural networks, which are very much inspired by the interconnected neurons present in the human brain. These networks have multiple layers, allowing them to learn patterns in a hierarchical way, from simple features to incredibly abstract concepts. This is the foundation upon which all models like Google’s Gemini, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, MetaAI and various are built.
Part 2: The Engine Room: How Generative AI Really Works
So, how do we go from recognizing patterns to generating a brand-new poem or writing functional code? This is the leap to Generative AI(ChatGPT, Gemini, etc). To understand this, let’s step away from a search engine(Google, Bing, etc) analogy.
A search engine is like a super-fast librarian. You ask it a question, and it scours its indexed library to find existing books and pages that match your keywords. It retrieves information.
A Generative AI is like a super-apprentice author. This author has read the entire library, internalized the knowledge, style, and structure, and when you ask a question, they synthesize that knowledge to write a completely new, custom paragraph just for you.
Here’s the step-by-step process of how this “writing” happens:

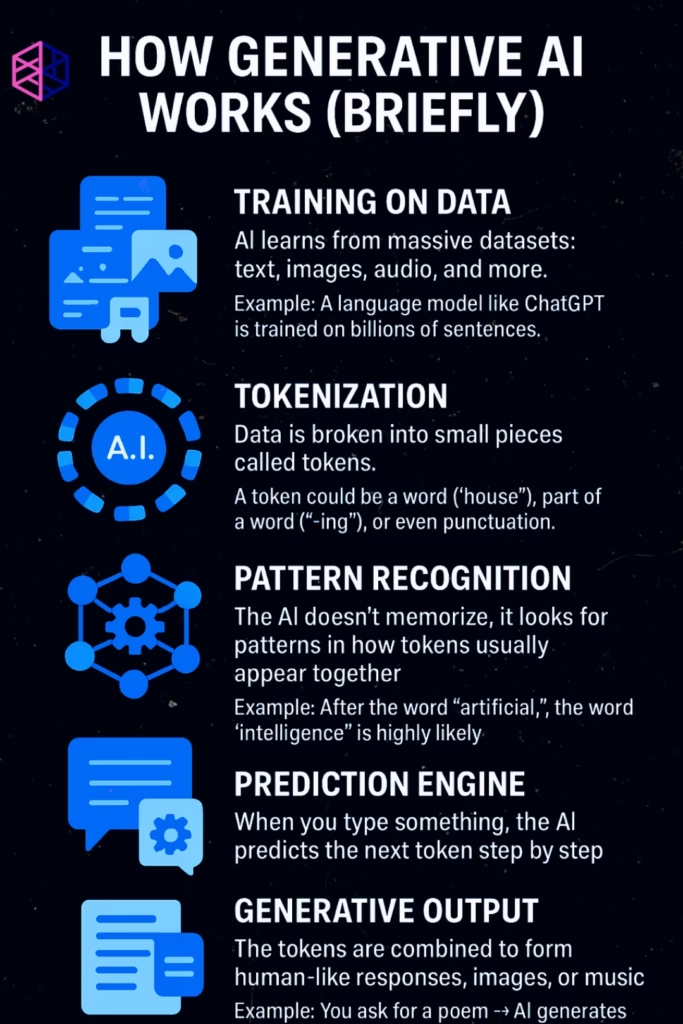
Step 1: Deconstructing the World (Input & Tokenization)
First, the AI has to understand your request. It can’t read text or see images like a human. It speaks one language: math. So, it breaks down your input into numbers.
- Tokenization: Imagine your question is a LEGO structure. Tokenization is the process of carefully breaking it down into individual LEGO bricks, called tokens. For text, a token might be a word (“cat”), or maybe a part of a word (“-ing”), or just a single character.
- Embedding: Each token is then converted into a list of numbers called an embedding. This isn’t a random ID; it’s a rich numerical representation that captures the token’s semantic “vibe” or for us which is meaning. Tokens with similar meanings, like “happy” and “joyful,” will have mathematically similar embeddings. This is how the AI grasps nuance.
Step 2: Finding the Connections (Processing & Attention)
Once your input is a sequence of meaningful numbers, it’s fed into the neural network. The breakthrough technology powering modern GenAI is the Transformer architecture, and its secret sauce is the Attention Mechanism.
Think of “attention” like using a highlighter. When you read the sentence, “I’m taking my dog to the park, but he doesn’t like the rain,” your brain instantly knows “he” refers to the “dog.” The attention mechanism does exactly this. It analyzes the entire input and weighs the importance of every token relative to every other token, allowing the model to track context, relationships, and grammatical nuances, even across very long texts.
This processed information then flows through the deep layers of the neural network, where increasingly complex patterns and relationships are identified. This is the “thinking” phase.
Step 3: Creating Something New (The Generative Process to produce answers)
This is the most crucial part of the process. The AI doesn’t have an answer stored anywhere, it doesn’t display any stored answers. It generates one, token by token as token is the only thing AI understands that too in number form.
Based on its understanding of the prompt given by you, the AI predicts the most probable first token of the response. Once that token is chosen, it becomes part of the context. Then, the AI predicts the most probable second token, given your prompt and the first token it just generated. This continues, chaining predictions together to build coherent sentences, paragraphs, code, or other outputs.
It’s a highly sophisticated game of “what comes next?”, guided by the trillions of patterns learned during training. A dash of controlled randomness (a parameter called “temperature”) is often added to this process, allowing the AI to be creative and avoid giving the exact same robotic answer every time.
This is synthesis, not retrieval. It’s the difference between finding a fact and writing an essay. But before all this comes the most critical and the most important part, the beginning of AI which is Training on Data, The model (AI) is being trained on a large dataset based on requirements, this training makes the AI eligible to think and learn accordingly.

Part 3: The AI Revolution: Impact on Our World 🌍
This powerful capability is a double-edged sword, bringing both unprecedented efficiency and significant disruption. The data tells a compelling story.
The Efficiency Revolution (The Boon)
AI is acting as a massive productivity multiplier across industries.
- A Harvard study found that management consultants using AI completed tasks 25.1% more quickly and with over 40% higher quality.
- In customer service, AI-augmented agents can handle 13.8% more issues per hour.
- Developers using AI coding assistants can be significantly more productive, with some studies showing a 126% increase in projects completed per week.
- Economically, the impact is staggering. Projections from IDC suggest AI could add nearly $20 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
The Great Disruption (The Threat)
The flip side of this efficiency is the transformation of the job market.
- A Goldman Sachs report estimates that Generative AI could automate tasks equivalent to 300 million full-time jobs globally.
- The World Economic Forum predicts a period of churn, with 83 million jobs potentially eliminated by 2027, even as 69 million new ones are created.
- The roles most at risk are those heavy on routine and data processing. Office and administrative support jobs see nearly half (46%) of their tasks as vulnerable to automation.
- Conversely, jobs requiring high emotional intelligence (therapists, teachers), complex manual skills (electricians, surgeons), and strategic leadership (CEOs) are far less exposed.

Part 3.5: The Creative & Automation Boom of AI
AI Media Generation 🎨🎬🎤
AI isn’t just answering questions or writing code anymore—it’s becoming a creator in its own right. Today, Generative AI is used to produce all forms of media:
- Images & Art → Tools like DALL·E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion can turn a simple text prompt into detailed, realistic images or artistic illustrations. Imagine describing a “futuristic city at sunset,” and within seconds, an AI has already painted it for you.
- Video → Platforms like Runway, Pika Labs, Google Veo and etc now generate cinematic-quality short films or edit videos automatically. What once required a studio, camera crew, and heavy editing software can now be done by a student with a laptop in their dorm room.
- Audio & Voice → AI can clone voices, create background music, or even generate entire songs (Suno, Aiva). Podcasters and video creators already use it to remove noise, change voices, or translate content into multiple languages.
- 3D & Virtual Worlds → Game developers and architects use AI to instantly generate 3D environments and models, saving weeks of manual work.
This is “democratized creativity.” A single creator now has the power of an entire designing team, which is revolutionizing industries like advertising, film, gaming, education, and many others at lightning speed.
AI Automations 🤖
On the other side of AI’s impact is automation—machines not just creating, but also doing.
- Business Workflows → AI chatbots are replacing traditional customer service, answering questions 24/7. In offices, robotic process automation (RPA) tools handle repetitive tasks like payroll, invoicing, and report generation.
- Personal Productivity → Modern assistants like ChatGPT with plugins or Google’s Gemini can summarize documents, draft emails, create presentations, and even schedule meetings automatically. It’s like having a digital secretary.
- Physical Automation → AI-driven robots are now common in warehouses (Amazon uses thousands to move goods), while autonomous vehicles and drones are being tested for deliveries and transport.
- Healthcare → AI assists doctors by analyzing X-rays, predicting patient risks, and even suggesting possible treatments. This reduces delays and allows doctors to focus more on direct patient care.
In short, AI is moving from being just a thinking machine to a working machine. AI is no longer just thinking—it is doing. This automation wave is quietly transforming businesses and daily life, making systems faster, cheaper, and often more reliable.

Part 4: The Path Forward: Navigating Our AI Future
So, where do we go from here? The answer depends on who you are.
For the Freshers, Student, or Curious Minds:
Their goal isn’t to compete with AI, but to collaborate with it. Focus on developing your uniquely human skills: critical thinking, creativity, complex problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. Learning how to effectively use AI tools—what we now call prompt engineering—is quickly becoming a fundamental skill, just like knowing how to use a web browser. Be curious, keep learning, and see AI as your co-pilot.
For the Experts, Developers, or Business Leaders:
These are the architects of this new era. The focus must be on responsible AI development. This means actively working to mitigate biases in training data, ensuring transparency in how AI models make decisions (explainability), and building systems that are safe and robust. Their challenge is to steer this technology toward augmenting human potential and solving real-world problems, ensuring the benefits are shared broadly.
Conclusion
AI is not a simple story of utopia or dystopia. It is a tool—arguably the most powerful one humanity has ever created. It reflects the data we train it on, the goals we give it, and the values we embed within it. The journey ahead isn’t a battle of human vs. machine, but an evolution toward human + machine. The numbers tell us change is here and it’s accelerating. The choice we have is how we meet it: with fear, or with a proactive vision for a future where technology empowers us all.